In the past, most B2B sales were conducted face-to-face – perhaps in a prospect’s conference room or at a golf course. Many deals are closed today without the buyer and seller meeting face-to-face, a practice known as inside sales.
The shift to remote sales accelerated during the pandemic. But it will only continue to grow. Gartner predicts that by 2025, 80% of B2B sales interactions will occur via digital channels.
By 2025
When it comes to inside sales, you may have questions like:
- What is inside sales?
- What do these teams do?
- How is it different from outside sales?
- What skills and tools do reps need for success?
We’ll answer these questions (and more) in this post.
What is inside sales?
There’s no doubt you’ve heard the term “inside sales.” But what is it?
It’s a model in which reps do their jobs from “inside” an office rather than face-to-face in the field. Some reps work from a company office, some from home, and others from both “inside” locations.
Inside sales teams leverage technology to connect and engage with prospects. Some methods inside sales reps use to engage with prospects include:
Phone calls
Video conferencing
Social media
Other online channels
Conversely, outside sales reps rely on face-to-face conversations. We’ll examine the difference between inside and outside sales later.
Today, inside sales (also referred to as remote sales) have become the dominant model of B2B sales, especially in industries such as technology and software as a service (SaaS). It’s also gaining popularity in B2C sales, especially for high–priced, big-ticket items.
Why an inside sales strategy is important
Inside sales teams are a critical part of the revenue organization. But why is it so important?
There are several reasons why revenue organizations are investing in these strategies. Let’s take a look at a few that top the list.
Meeting buyer expectations and preferences
While in-person sales were once the default, many B2B buyers prefer to engage with sellers remotely. Consider that in 2017, 20% of industrial companies preferred digital interactions and purchases. Today, that number has grown to 67%.
In 2017
In 2024
of industrial companies preferred digital interactions and purchases
With a strong strategy, organizations can engage with prospects how they want to engage. When you meet buyers’ expectations, they’re more likely to stay engaged – and make a purchase.
Faster sales cycles
Traveling back and forth to a prospect’s office takes a lot of time, so sales cycles tend to be long in outside sales.
When sales reps sell from an office, they can close deals faster and work on multiple opportunities concurrently.
With inside sales, reps can close more deals faster, which is great news for your bottom line.
Lower cost per sale
Any sale has costs. However, the costs associated with inside sales are significantly lower than those associated with outside sales.
According to the Harvard Business Review, when appropriately utilized, inside sales “reduces cost-of-sales by 40-90% relative to field sales, while revenues may be maintained or even grow.” In other words, an inside sales strategy positions you to grow sales while decreasing costs.
What do inside sales reps do?
Inside sales reps – like any sellers – aim to make connections with qualified prospects, understand their needs, and work to deliver solutions that address their key challenges. What sets these reps apart is where they accomplish this work.
Reps sell from a corporate or home office rather than in the field.
Inside sales roles
Typically, the inside sales team has several different roles, each responsible for a different stage of the sales process.
The makeup of team varies from organization to organization. However, there are some common roles.
SDRs are typically focused on inbound sales. These are warm leads from prospects who have taken action to indicate their interest. Some such actions include downloading a report, requesting a live demo, interacting via live chat on the company website, or registering for and attending a webinar. An SDR will make initial contact with these leads and then pass along the qualified ones to an account executive (AE) on the team.
BDRs are typically focused on outbound sales. In other words, they make cold calls and send cold emails to connect with qualified prospects. Often, these are enterprise accounts. Once they’ve made initial contact and qualified a lead, they’ll pass it along to an AE.
AEs are responsible for taking leads from BDRs and SDRs and guiding them through the sales cycle.
An inside sales manager oversees a team of inside sales reps. They have myriad responsibilities, including setting sales goals, forecasting, hiring, and delivering personalized coaching that helps each seller understand inside sales best practices – and reach their full potential.
Different factors, including industry, prospect company size, product or service offering, and geography often segment teams. Segmentation depends on the needs of the revenue organization.
What’s the difference between inside and outside sales?
In the business world, “inside sales” and “outside sales” are two phrases thrown around a lot. But what’s the difference?
Both are responsible for closing deals. They do so by getting to know a prospect’s needs – and then working to address them.
However these two teams go about it differently.
Outside sales teams – also referred to as field sales – meet with prospects face-to-face. Meetings could happen at a prospect’s office or another location, like a tradeshow booth or industry event. Inside sales, on the other hand, engage with prospects remotely. Inside sales reps can guide a deal to the finish line without ever being in the same room as the prospect.
Outside sales teams rely on face-to-face meetings to build relationships and close deals. They can schedule these meetings by cold calling, seeking referrals from existing customers, or visiting an office location.
Inside sales teams rely on other channels to engage with buyers, including phone calls, video conferencing, email, and social media. Many teams also use digital sales rooms to communicate and collaborate with prospects. Digital sales rooms are especially effective when buying committees are large—and they often are. According to Forrester, 63% of purchases involve more than four people. In 2017, that was the case for 47% of purchases.
| Inside sales | Outside sales | |
|---|---|---|
| Also known as | Virtual sales | Field sales |
| Work location | At company or home office | In the field, which may include a prospect’s office, another facility like a factory or plant, trade show, or industry event |
| Key customer engagement channels | Phone calls, video calls, emails, social selling | In-person meetings |
What are the characteristics of a successful inside sales rep?
To be successful in their roles, reps must master certain skills and competencies. It’s important to identify these skills. A good way to do this is to closely examine your most successful reps and determine what they’re doing differently. You can document key skills, characteristics, and behaviors in an ideal rep profile (IRP).
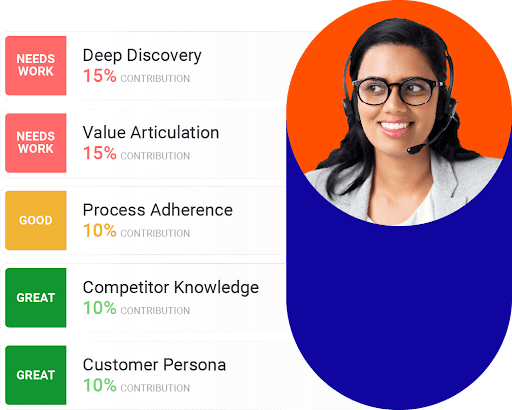
Your IRP can guide your hiring process. It should also guide the ongoing sales training, sales enablement, and coaching you deliver to ensure your inside sales reps are set up for success.
So, what are the skills and characteristics needed to succeed? The short answer is, it depends. However, certain characteristics are required for just about any rep to make their sales quota.
Product knowledge
Reps must be experts in their product and service offerings. This requires ongoing sales training, enablement, and coaching as product offerings always evolve.
Of course, reciting a list of product features isn’t enough. Instead, reps must articulate how a specific solution can solve a prospect’s key challenges.
Research skills
B2B buyers are no longer satisfied with generic information and experiences. Instead, they expect every experience to be tailored to them.
Reps must be prepared to deliver value right from the start. First, they must do their homework.
With the right tools, reps can uncover much information independently. However, they should also be skilled at asking the right questions to uncover key information.
Cold calling and cold outreach
Cold calling and cold outreach are key. Reps must be comfortable picking up the phone or contacting a prospect via email and skilled at getting prospects to engage.
They should also be experts on their organization’s buyer personas and know what questions to ask to determine whether a prospect is a good fit. That way, account executives spend their time with the most qualified leads.
Discovery
Before presenting a solution, reps must understand a prospect’s pain points. They must also have strong discovery skills to determine a customer’s key opportunities and challenges quickly.
Objection handling
Reps are bound to face objections from prospects. But objections don’t necessarily mean a deal is dead in the water.
They must be equipped to address and overcome key objections. When a rep expertly navigates objections, the prospect is more likely to purchase.
Communication skills
Every sales rep needs strong communication skills, but inside sales reps must also be skilled at effectively communicating and building relationships remotely.
They must be able to communicate clearly with prospects. However, they must also be great listeners and know what questions to ask to get prospects talking.
Internal communication skills are also critical for inside sales reps. A sales rep must know when to involve others in the conversation and effectively brief them before engaging with the prospect.
Technology skills
Reps require the right technology to be effective and efficient. For example, a rep may depend on a sales enablement platform to learn about a new product and access the right content to share with prospects. They may also rely on a customer relationship management (CRM) tool to stay on top of the many moving pieces of a deal.
Reps need to be familiar with the different tools of the trade and willing (and able) to learn the unfamiliar ones quickly.
Data-driven
Reps must take a personalized approach to selling. While it’s important to follow the established sales process, they must also be adept at examining the data available to them and adapting accordingly.
Artificial intelligence (AI) can make this easier. For example, AI can analyze data to suggest what step an inside sales rep should take next – such as sharing content that’s worked in a similar sales scenario.
What are the tools needed for success?
To be successful, inside reps need certain skills and behaviors. An inside sales strategy also requires the right tools.
Inside sales software stacks vary from company to company. However, there are certain tools nearly all inside sales reps need to achieve their sales quota.
Building relationships is key to any sales strategy. A CRM like Salesforce helps sales reps manage the many moving pieces of these relationships.
Reps need to master certain skills to be successful. An integrated sales enablement platform like Mindtickle enables inside sales teams to can access the training, information, and coaching they need to build key skills. A sales enablement platform like Mindtickle also incorporates sales content management, which enables sales reps to quickly and easily find the right content for any sales scenario.
Content is an important tool for moving deals forward. But it can be challenging for sales reps to find the right sales content. A sales content management tool can help inside sales reps surface content proven to improve outcomes.
Some inside sales interactions take place via phone calls. However, video conferencing allows reps to see prospects face-to-face and deliver more dynamic presentations and demos.
Inside sales reps are responsible for finding and connecting with good-fit prospects. The right prospecting tools make this easier. For example, LinkedIn Sales Navigator enables inside sales reps to leverage their LinkedIn networks to connect to the right people at the right companies.
Scheduling appointments is essential to inside sales reps. But finding a time can be time-consuming. An appointment scheduling tool automates the process, saving reps’ time.
Mindtickle empowers winning inside sales teams to close more deals
A strong sales inside team can make a huge impact on revenue growth. But the role of a rep isn’t easy.
They face increasingly complex markets and buyers with extremely high expectations. Revenue organizations must ensure inside sellers have the right skills and tools to overcome key challenges and close more deals.
With Mindtickle, teams have access to the training and enablement needed to master the skills needed for success. Reps can also access reinforcement, practice opportunities, and coaching that help ensure learning sticks.
In the world of B2B inside sales, content is king. Mindtickle enables sales reps to surface the right content for any selling scenario quickly.
Create a team of inside sales superstars
Ready to see how Mindtickle can boost the effectiveness and efficiency of your inside sales team?
Request a Demo

 By Helen Waite
By Helen Waite

 By Rahul Mathew
By Rahul Mathew